It is a batch of SQL statements that you can run by executing the batch.
Basically you declare a command variable and execute the command. The Command variable has the executable T-SQL code. The executable code may also contain the following:
- System Stored Procedure
- User defined stored procedure
- CLR stored procedure
- Scalar valued user-defined function
- Extended stored procedure
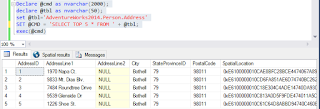
Let me first give an example which is often used to demonstrate the use of Dynamic SQL. I am using SQL Server 2016 but using a database imported from SQL Server 2014.
The first line of code declares a variable @cmd of data type characters
The second line declares a variable @tbl also of data type characters
The third statement sets a value for the @tbl variable which in this case AdventureWorks2014.Person.Address table. This statement does not require the context of AdventureWorks2014, but can be run from 'master'
The fourth statement declares what the @cmd variable should do when executed. It is just a SELECT statement that selects the top 5 rows from the Person.Address table.
You can see that this dynamic SQL returns the results requested.
Read the MSDN article here:
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ms188332.aspx?f=255&MSPPError=-2147217396
No comments:
Post a Comment