The readers of my articles on several forums asks questions regarding something or the other and I do answer them promptly. However I feel the answers should be shared among a larger group of people. I think this blog will make this possible.
Showing posts with label mutable. Show all posts
Showing posts with label mutable. Show all posts
Tuesday, July 10, 2018
Thursday, July 5, 2018
What are the differences between a list and a tuple in Python?
You have seen what a list is. Tuple is a standard data type for sequence and it is immutable.
According to Python site:
"Tuples are immutable, and usually contain a heterogeneous sequence of elements that are accessed via unpacking (see later in this section) or indexing (or even by attribute in the case of namedtuples). Lists are mutable, and their elements are usually homogeneous and are accessed by iterating over the list.
"
The following table prepared using:
Python 3.7.0b5 (v3.7.0b5:abb8802389, May 31 2018, 01:54:01) [MSC v.1913 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
shows the differences. There is little you can do with a tuple because of its immutablity compared to Lists. Of course define them correctly.
According to Python site:
"Tuples are immutable, and usually contain a heterogeneous sequence of elements that are accessed via unpacking (see later in this section) or indexing (or even by attribute in the case of namedtuples). Lists are mutable, and their elements are usually homogeneous and are accessed by iterating over the list.
"
The following table prepared using:
Python 3.7.0b5 (v3.7.0b5:abb8802389, May 31 2018, 01:54:01) [MSC v.1913 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
shows the differences. There is little you can do with a tuple because of its immutablity compared to Lists. Of course define them correctly.
Saturday, February 18, 2017
What are mutable and immutable variables in F#?
If I assign a value to a variable and then later in the program I assign another value to the same varible the program does not care if it is a mutable variable. However if it is immutable, the program does not accept it. Hence immutable variable is one which is solidly bound to its value.
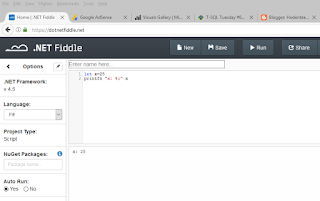
Let me take you to the .NET Fiddle site so that you can run it yourself and see the result.
First of all assignment to a variable in F# has the following syntax:
let x=25
The above statement assigns a value 25 to the variable x. I can print it to the screen using the second statement (printfn "x: %i" x) because x is an integer.
Next I assign a value of 45. You can see the error in this statement immediately. Hence value of x is immutable.
Now how can I assign a mutable value?
Well, F# uses the keyword mutable as shown here:
let mutable x=15
Now x has a value which can be changed later as shown in the next image. The first statement sets a value 15 for the variable x and the second statement prints it.
The third statement assigns a new value to it, namely 20 and the fourth line prints it. Observe carefully the new value assignment, a backward going arrow.
Let me take you to the .NET Fiddle site so that you can run it yourself and see the result.
First of all assignment to a variable in F# has the following syntax:
let x=25
The above statement assigns a value 25 to the variable x. I can print it to the screen using the second statement (printfn "x: %i" x) because x is an integer.
Now how can I assign a mutable value?
Well, F# uses the keyword mutable as shown here:
let mutable x=15
Now x has a value which can be changed later as shown in the next image. The first statement sets a value 15 for the variable x and the second statement prints it.
The third statement assigns a new value to it, namely 20 and the fourth line prints it. Observe carefully the new value assignment, a backward going arrow.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)